25
showed a decreased risk for early ARM in subjects with
high dietary intake of vitamin E or zinc, by compari-
son with those with low intake
(29)
. A European supple-
mentation study would be needed to better assess the
benefit of antioxidant supplementation in European
populations.
A more recent research domain evaluated the role of two
carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, in the protection of
the retina and the lens. These carotenoids accumulate
in the macula, where they are known as the macular
pigment
(30)
. Besides their antioxidant properties, they
probably act as a filter against the phototoxic effects of
blue light
(30)
. To date, five epidemiological studies have
assessed the associations of the risk of AMD with plasma
concentration of lutein and zeaxanthin
(31-35)
. As shown
in Fig. 1, all five studies showed a decreased risk for
AMD in subjects with high plasma concentrations of
lutein and zeaxanthin, although the association was sta-
tistically significant only in 2 studies
(32-35)
. With regard
Modifiable risk factors for AMD
to dietary intake, four prospective population-based
studies were published
(29,36-38)
. These studies assessed
the risk for developing AMD (in subjects initially free
of AMD), according to their dietary intake of lutein
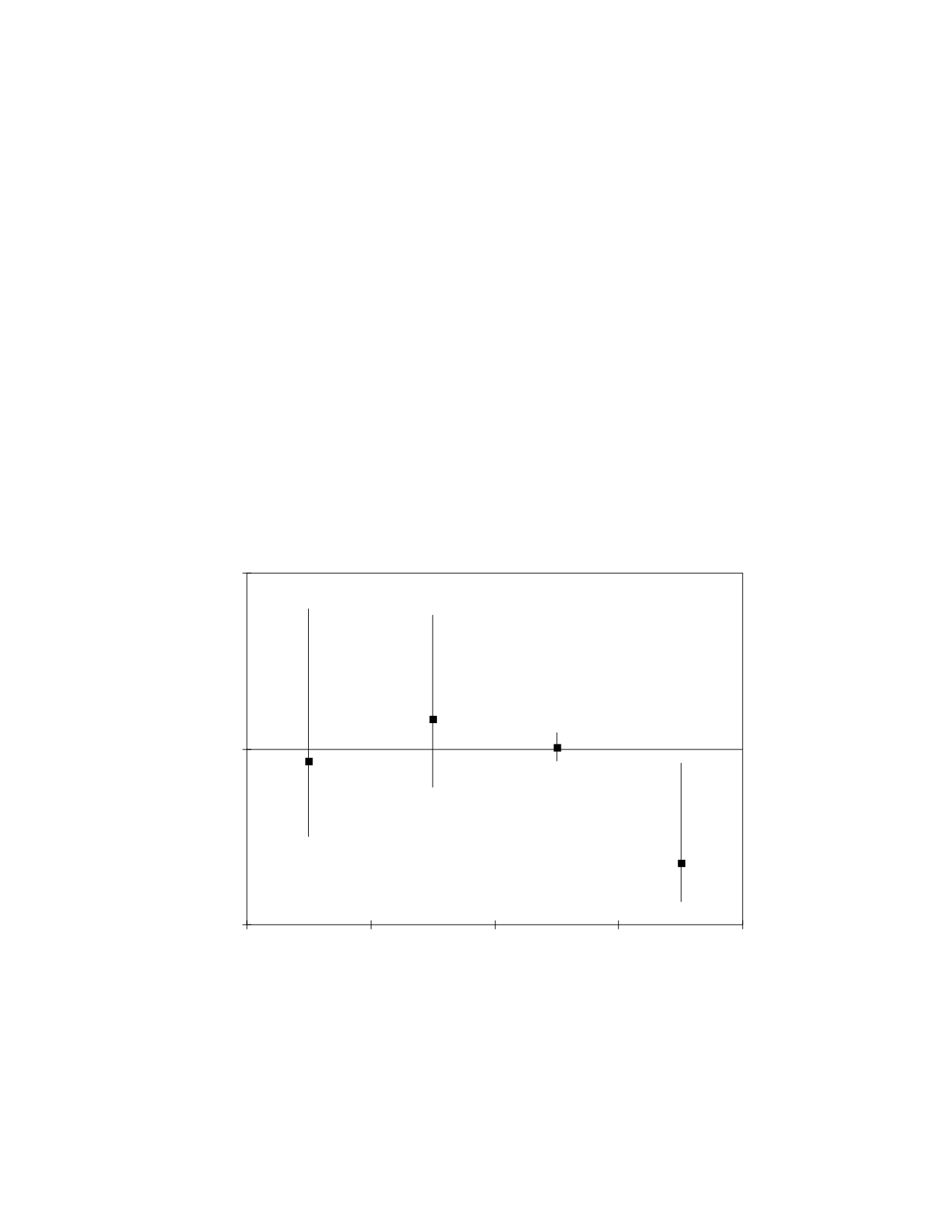
and zeaxanthin. As shown in Fig. 2, the results for these
dietary studies are less clear than for those on plasma
measurements. Only one study found a significantly
reduced risk for AMD in subjects with high dietary
intake of lutein and zeaxanthin
(38)
. However, dietary
assessment methods rely on the subjects’ memory and
perceptions and face the difficulties of the extreme day-
to-day variability of human diet, the bias in reporting
due to social standards and nutritional recommenda-
tions and the estimations of nutritional contents of
food items. Biomarkers have the advantages of being
objective, and of taking into account individual varia-
tions in bioavailability and metabolism. For instance,
smoking and obesity are known to decrease the bio-
availability of carotenoids
(39-40)
. Despite normal dietary
0
1
2
Beaver Dam
Health
Professionals
Rotterdam Blue Mountains
Figure 2. Associations of the risk for AMD with dietary lutein and zeaxanthin, in published epidemiological prospective studies. References of the
cited studies: Beaver Dam
(36)
; Health Professionals
(37)
; Rotterdam
(29)
; Blue Mountains
(38)
.


