220
cytoskeleton of newly formed cells is sensitive to CA-4-P,
whereas the cytoskeleton of mature cells is not. This
appears to underlie the selective shutdown of neovascular
vessels compared to that of normal vessels.
Currently Zybrestat has been tested intravenously-
administered in clinical studies in patients with forms
of macular degeneration. The topical administration
cells identical to those induced by VEGF with increase in
endothelial cell proliferation and reduction of apoptosis
what leads to increase in capillary network formation
(34)
.
Antagonists of nAChR abolish the proangiogenic effect
of nicotine nAChR and VEGF: Two distinct but interde-
pendent angiogenesis pathways
(35)
.
Neutralization of VEGF resulted in a significant but
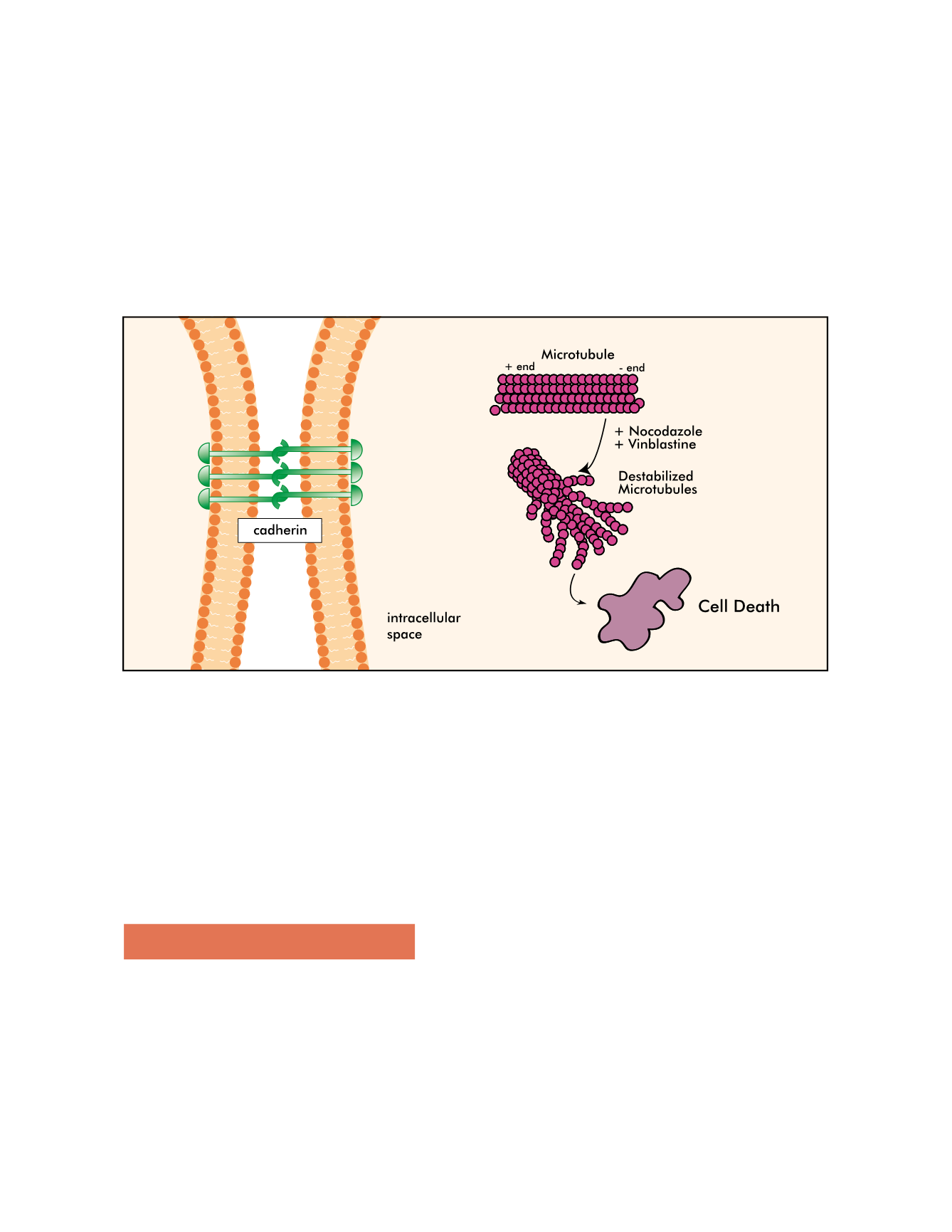
Figure 4 - The mechanism of action is a vascular disrupting agent (VDA) by a dual action: tubulin depolymerizing agent and cell junction disruption.
These actions upset the physical structure of the existing blood vessels.
is being tested in animal studies. A phase II study in
patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV)
is initiated
(33)
. Current therapies active against wet AMD
appear to have limited benefits in patients with PCV,
and OXiGENE (Oxigene inc. San Francisco) believes
the abnormal vasculature in the retina and choroid that
contributes to PCV patients loss of vision may be suscep-
tible to treatment with Zybrestat.
9. Anti-nicotine agents
Nicotine has a potent angiogenic effect. It has two distinct
but interdependent pathways for angiogenesis; nAChRs
are involved in the native angiogenic response, and this
pathway is distinct from those triggered by VEGF or
FGF.
Nicotine induces morphological changes in endothelial
not complete inhibition of nAChR-mediated network
formation.
9.1 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists
Non-selective cholinergic agonists such as nicotine have
been shown to induce angiogenesis, enhancing tumor
progression. Moreover,
α
7 AChR (nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor) selective antagonists such as
α
-bungarotoxin
and methyllycaconitine as well as the non-specific
antagonist mecamylamine have been shown to inhibit
endothelial cell proliferation and ultimately blood vessel
formation. Such pharmacologic properties can lead to the
discovery of new specific cholinergic antagonists as anti-
AMD therapies. Conversely, the pro-angiogenic effect of
specific agonists can be used to treat diseases that respond
to revascularization such as diabetic ischemia and athero-
sclerosis, as well as to accelerate wound healing
(36)
.


