193
Combined Treatment
rienes and prostaglandins that cause vasodilatation,
increased permeability and oedema.
They also have an angiostatic effect by promoting a
decrease in extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover through
inhibition of plasmin activation. Plasmin activates
matrix collagenases and metalloproteinases (MMP’s)
that dissolve the capillary basement membrane and trig-
ger angiogenesis, with endothelial cell differentiation,
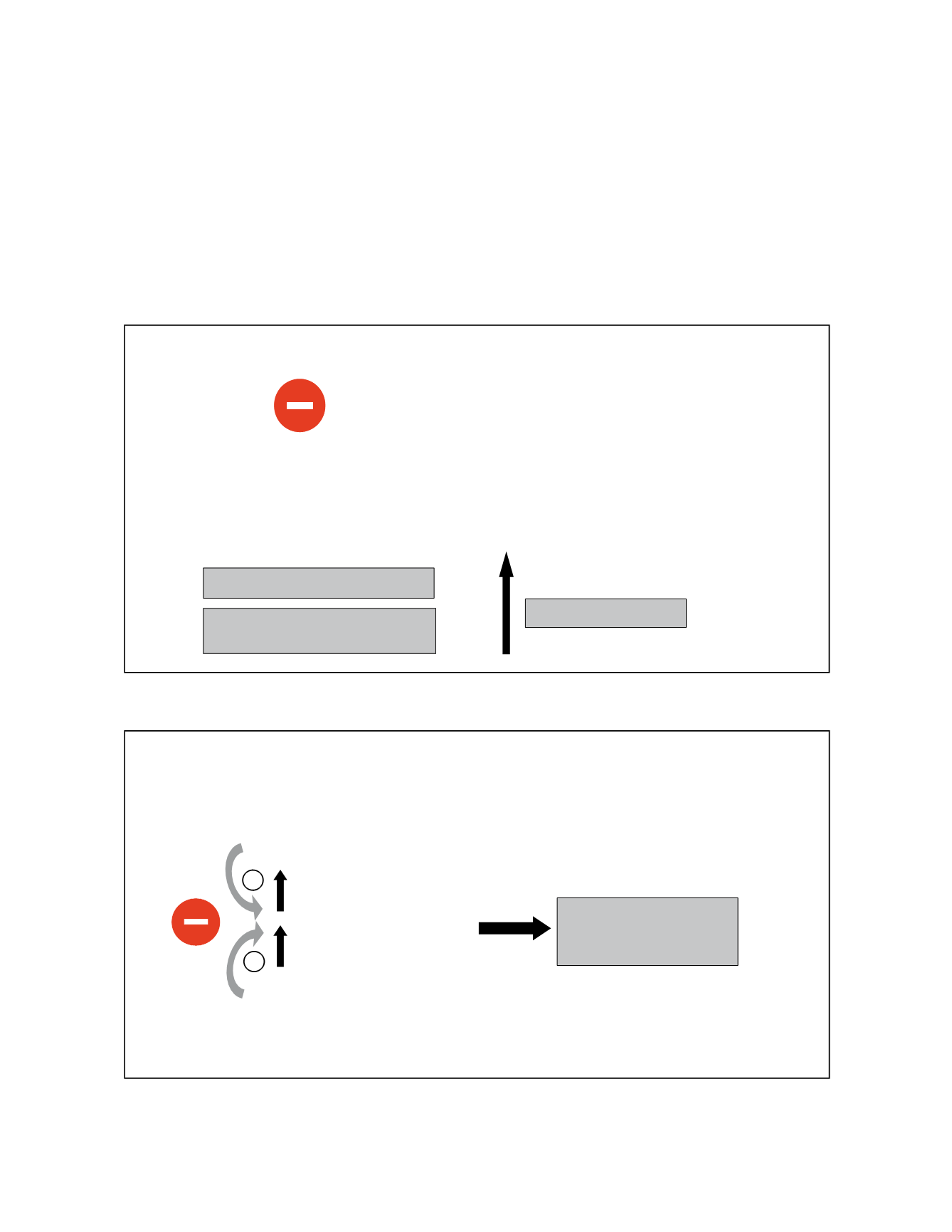
Figure 2 - Corticoids inhibit MMP’s (metalloproteinases) activity
Decreasing cellular cohesion
INCREASE
Vascular permeability
Decreasing barrier function of
electric charges
MMPs
- matrix metalloproteinases
(MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9)
. Extracellular matrix degradation
. Allow VEGF and other factors access to endothelial cells
Corticoids inhibit MMP’s
Figure 3 - Corticoids decrease VEGF, SDF - 1, ICAM - 1 and VCAM - 1 activity.
SDF-1
Butler et al. - J Clin Invest 2005
Inter Cellular Adhesion Molecule -1
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule -1
Funatsu et al. Ophthalmol. 2005
VEGF
ICAM-1
VCAM-1
+
+
Leukocyte stasis and
homing
Corticoids decrease VEGF activity
migration and proliferation (Fig. 2).
These agents also act on the interaction between
ICAM-1 (Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1) and leu-
kocytes, inhibiting recruitment of the latter, thereby
contributing to reduce the inflammatory component.
It is also thought steroids may act on SDF-1 (Stromal-
cell Derived Factor-1), inhibiting its action (Fig. 3)
(9,10)
.
Steroids also decrease the expression of Major Histo-


