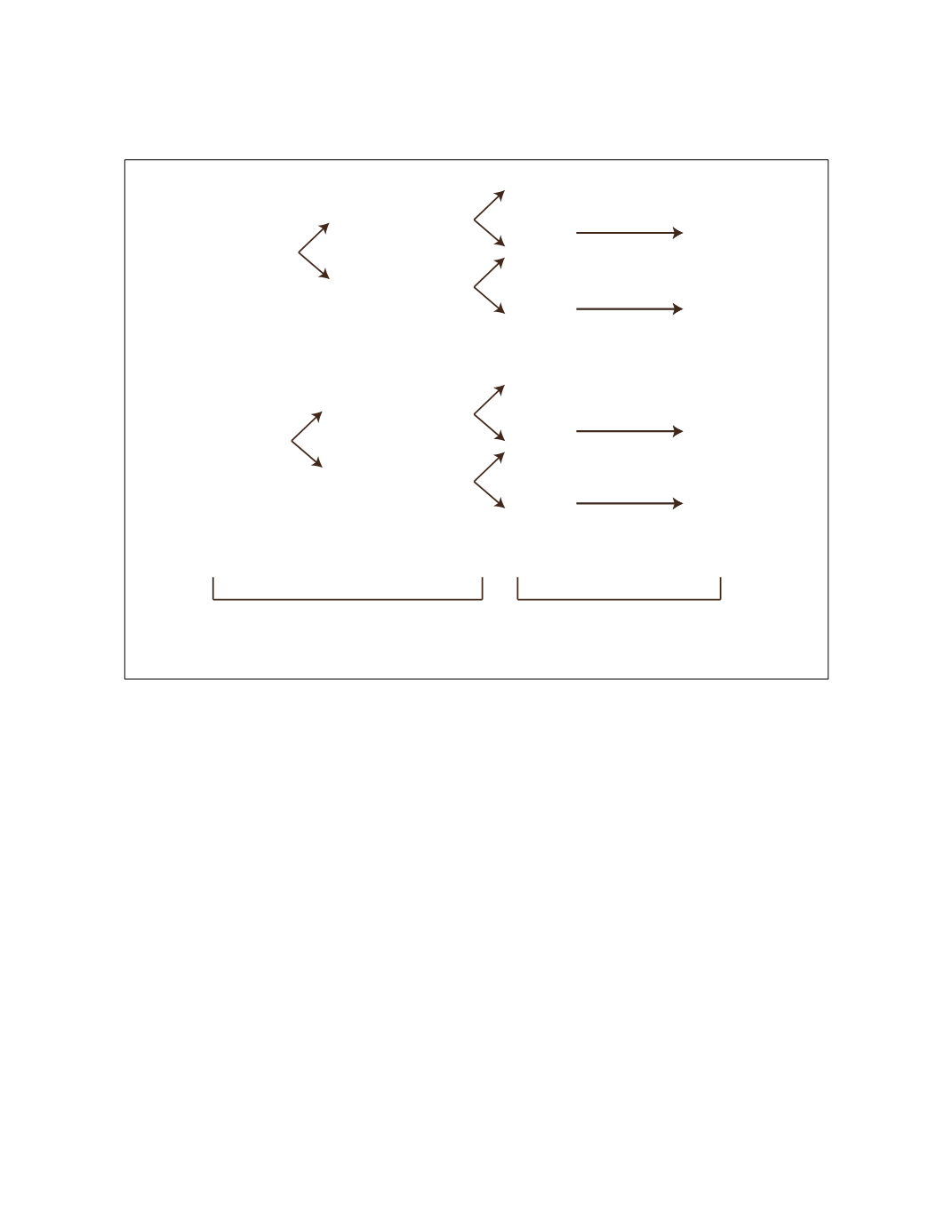
56
Right Eye
Left Eye
Large Drusen
No = 0
Yes = 1
1
1
Yes = 1
No = 0
No = 0
Yes = 1
1
1
Yes = 1
No = 0
Pigment Changes
Large Drusen
Large Drusen and
Pigment Changes
Pigment Changes
Patient Severity
Score = 4 Risk Factors
in the approximate sequence of: 0 factors, 0.5%; 1 factor,
3%; 2 factors, 12%; 3 factors, 25%; and 4 factors, 50%.
This scale may be useful clinically, either with ophthal-
moscopy or slit lamp biomicroscopy, or in less optimal
photographs using less complex grading procedures than
those used in AREDS.
For clinical purposes, as the number of risk factors
increases from 0 to 4, the 5-year risk of advanced AMD
in at least one eye increases in the easily remembered
approximate sequence of 0.5%, 3%, 12%, 25%, and
50%. Extensive drusen area, as seen on fundus photo-
graph, is the greatest risk factor for the progression of
AMD
(31)
. When examiners are asked to mentally aggre-
gate the amount of drusen occupying a given macular
subfield
(32)
, as in the International System, where drusen
areas were estimated to within 10% to 25% or 25% to
50%, and so on
(33)
, these semi-quantitative estimates
prove difficult for human observers. Clearly, there is a
need to implement more precise techniques to improve
the quality of data being gathered in clinical trials and
epidemiological studies.
8.2 Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography is the standard examination
for diagnosis and classification of conversion from early
ARM to exudative AMD.
8.3 Indocyanine green angiography
In AMD, digital indocyanine green (ICG) angiography
is a technique that may enable improved imaging of
occult CNV
(34)
. Hot spots are observed frequently in
retinal angiomatous proliferation (RAP), polypoidal
choroidal vasculopathy and focal occult CNV
(35)
. ICG
Table 1- Risk factors for AMD (from AREDS).


