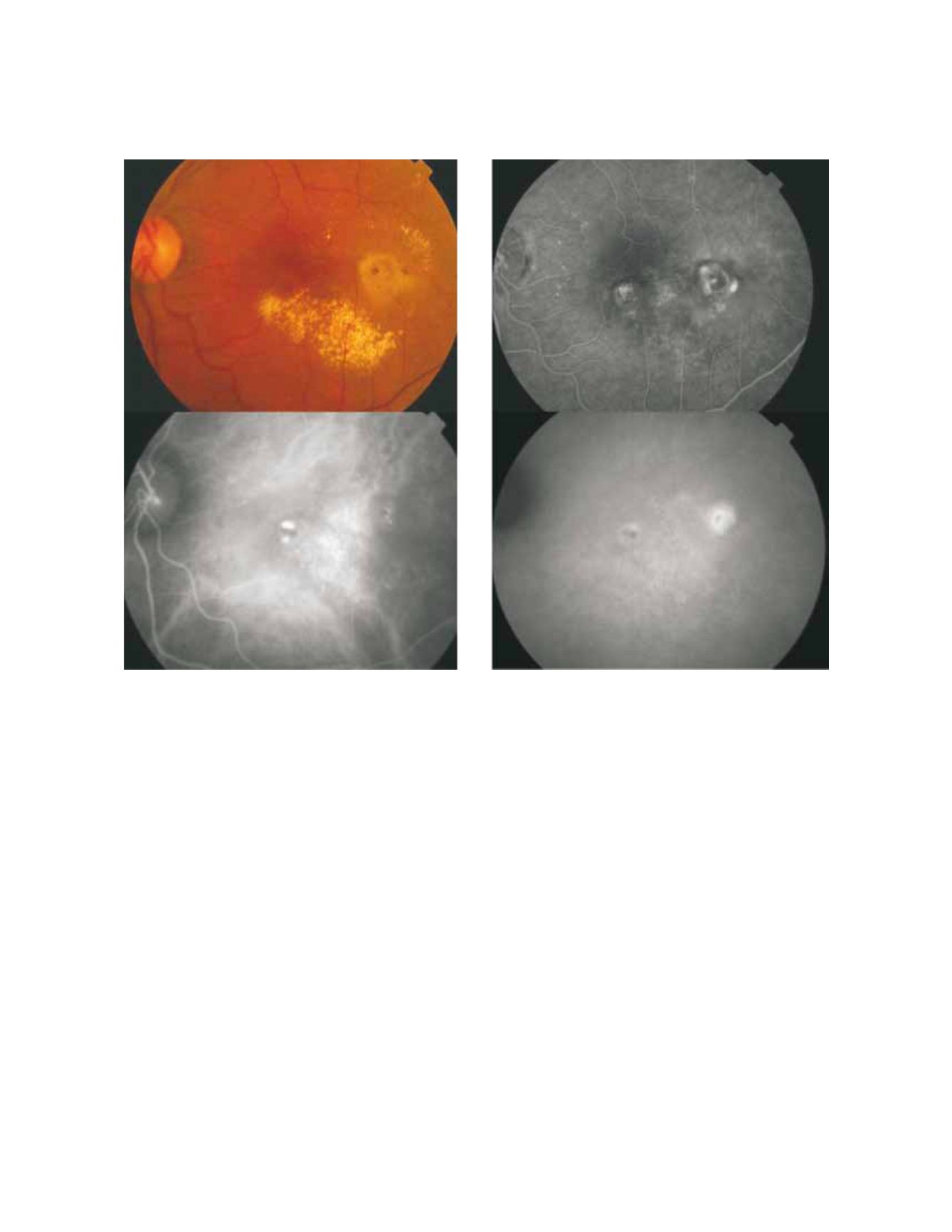
134
Figure 4: Fundus colour photography (A) reveals the presence of circinate lipidic exudation surrounding a redish-orange lesion temporal to the
fovea. Late phases fluorescein angiography (B) shows a diffuse leakage with juxtafoveal involvement and two focal areas of staining and leakage. Two
polypoidal foci separated by an abnormal choroidal vascular network are observed on ICG intermediate phase (C). Late phase ICG (D) shows an
hiperfluorescent plaque, a more temporal hot spot (active polyp) and a more nasal hypofluorescent spot with hyperflluorescent borders (apparently
inactive polyp).
serous or serous-hemorrhagic PED and/or neurosensory
detachment associated with extensive subretinal haemor-
rhages and circinate hard exudates (Fig. 1, 2, 4).
Fluorescein angiography alone is useful for PCV diagno-
sis. Neurosensory detachment and serous or sero-hem-
orrhagic PED may suggest the diagnosis but polypoidal
lesions are only visualized if the overlying pigment epi-
thelium is atrophic.
Intermediate or late leakage on fluorescein angiogra-
phy is very often diagnosed as occult choroidal neo-
vascularization with late leakage from undetermined
source or may be confused with chronic central serous
chorioretinopathy.
The characteristic PCV lesion in ICG is an inner abnor-
mal choroidal vascular network of vessels ending, in the
great majority of cases, in aneurysmatic dilatations.
The lesion may be juxtapapillary, macular or may be
rarely located in the midperiphery. Juxtapapillary lesions
often show, in early ICG images, a radial arching pat-
tern, and the vascular channels may be interconnected by
smaller spanning branches more numerous at the edge of
the lesions
(29)
. When the polipoydal lesion is located in
the macular area the vascular network often arise in the
macula and follows an oval distribution
(29)
. The area sur-
rounding the vascular network is hypofluorescent during
early phases of ICG and in late phase ICG angiography
often shows a reversal of the pattern: the area surround-
ing the polypoidal lesion becomes hyperfluorescent and
the centre shows hypofluorescence. In very late phases
ICG shows disappearance of the fluorescence (washout)
in non-leaking lesions (Fig.4-d)
(4,16,18,19)
.
OCT and particularly 3-D OCT is very useful for
A
B
C
D


