72
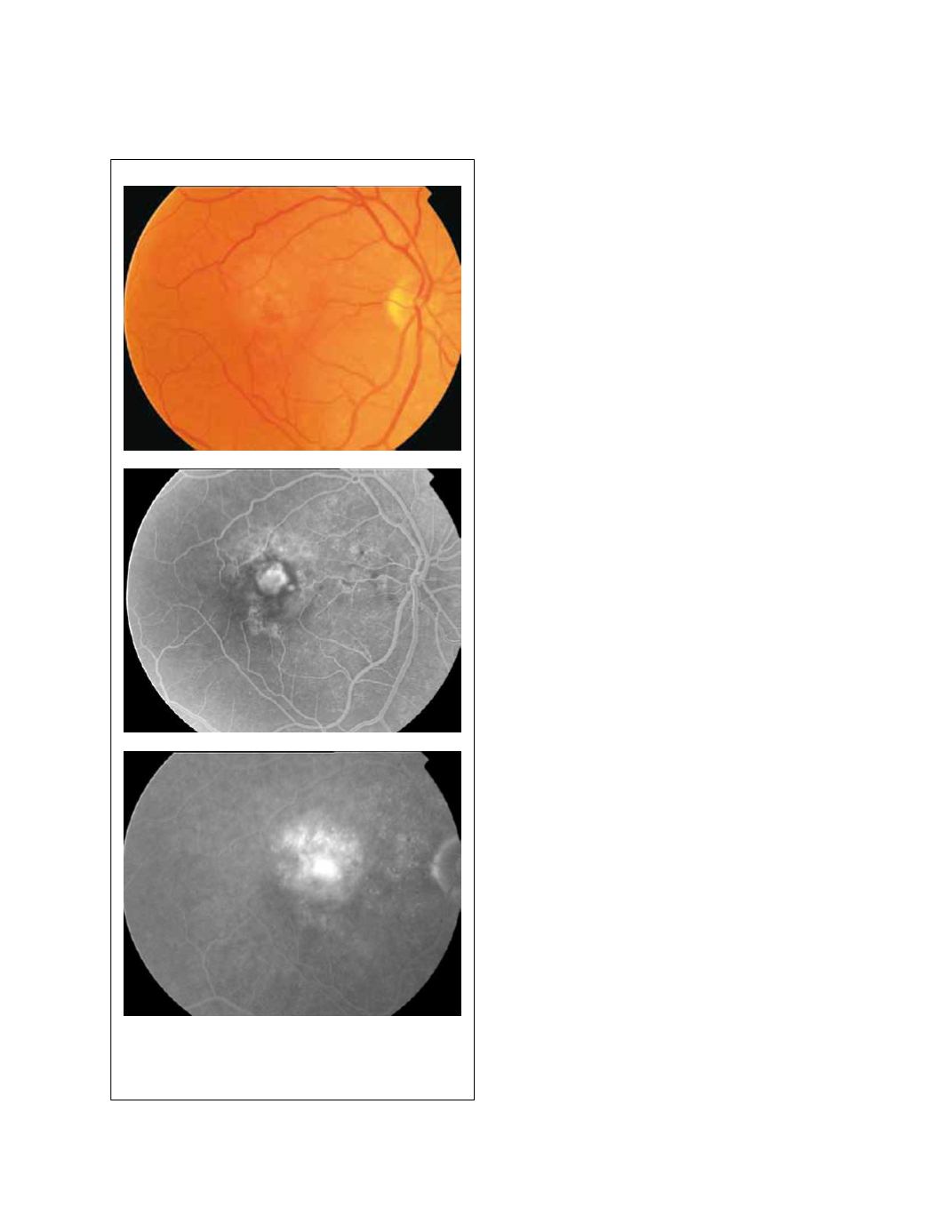
Figure 18 - Minimally classic CNV.
Importantly, larger classic CNV are associated to a poorer
visual prognosis since they represent long-term duration
of the pathological disorder. Classic CNV is an emergency
and it requires early treatment to halt the progression of
the disease. Without treatment, CNV tend to enlarge and
irreversible fibrosis appears (Fig. 16).
In the last decade of the last century, the advent of pho-
todynamic therapy (PDT) with verteporfin promoted a
classification of the lesions depending on the percent-
age of classic CNV. Thus, predominantly classic lesions
were defined as having 50% or more of the total lesion
size comprised of classic CNV (Fig. 17). On the other
hand, minimally classic lesions were characterized by
classic CNV occupying less than 50% of the total lesion
size (Fig. 18)
(12)
. The best results with PDT in wet AMD
patients were obtained in the treatment of predomi-
nantly classic lesions. Nowadays, in the antiangiogenic
therapy era, this classification has lost popularity among
ophthalmologists since lesion composition does not
seem to be as relevant as it was with PDT.
Lesion components associated with neovascular AMD
that can obscure the boundaries of CNV include changes
that block fluorescence, such as blood, fibrous tissue,
RPE hyperplasia, or RPE redundancy (from an RPE
tear). Likewise, CNV can be obscured by greater fluores-
cence from staining or pooling.
3.4 Occult CNV
Occult CNV has been categorized as fibrovascular PED
or late leakage of undetermined source
(13)
. Fibrovascular
PED (type I occult CNV) is defined as an irregular eleva-
tion of the RPE associated with stippled hyperfluores-
cence apparent 1 to 2 minutes after fluorescein injection
and ill-defined staining or leakage in the late frames
(Fig. 19-20). It differs from classic CNV in that the
early hyperfluorescence is not as bright and the boundar-
ies usually are indeterminate. Late leakage of undeter-
mined source (type II occult CNV) lacks a discernible,
well-demarcated area of leakage in the early angiographic
frames. Speckled hyperfluorescence with no visible
source becomes apparent 2 to 5 minutes after dye injec-
tion (Fig. 21).
3.5 Serous PED
Although serous PEDs can occur in the context of non-
neovascular AMD, most of them are related to CNV. On
fundus biomicroscopy, a serous PED appears as a round
or oval translucent elevation of the RPE. On FA, it is


