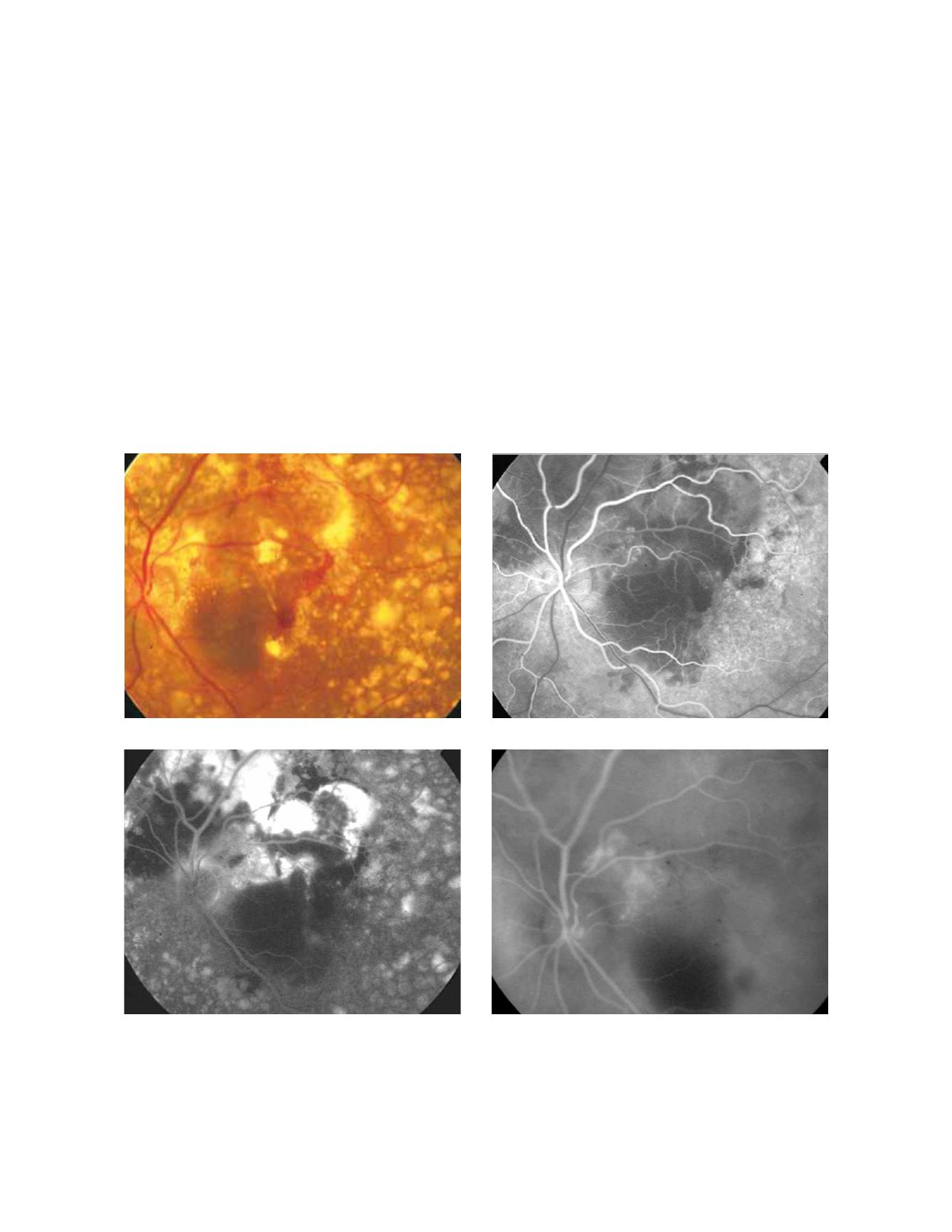
77
characterized by progressive and uniform hyperfluores-
cence from early frames with intense pooling of fluores-
cein in late phases (Fig. 22). PEDs with a notch usually
have occult CNV in the notch (Fig. 23). The association
of occult CNV and a serous PED is frequently termed
“vascularized PED”
(14, 15)
. On occasion, a serous PED is
associated to classic CNV (Fig. 24).
3.6 Retinal angiomatous proliferation
Retinal angiomatous proliferation (RAP) has been
described and classified by Yannuzzi et al.
(16)
. In RAP, the
vasogenic process originates in the retina and begins as
intraretinal neovascularization (stage I), which progresses
to subretinal neovascularization (stage II) and finally to
CNV (stage III). In some cases it is possible to find a
retinal-retinal anastomosis. Angiographically, early lesions
(stage I) show a focal area of intraretinal hyperfluorescence
with indistinct borders corresponding to the intraretinal
neovascularization and surrounding intraretinal edema
(Fig. 25). Sometimes, these early lesions can mimic the
appearance of a classic CNV. Later stages of RAP are often
classified as minimally classic or occult CNV.
In stage II, it is very characteristic to find a serous PED
with occult CNV associated to overlying cystoid macular
edema (Fig. 26). Indocyanine green (ICG) angiography is
often more useful than FA for the diagnosis and evaluation
of RAP lesions.
Figure 27 - Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy.
A
B
C
D
Fluorescein Angiography


