78
3.7 Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
In polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), the primary
abnormality involves the choroidal circulation, and the
characteristic lesion is an inner choroidal vascular network
of vessels ending in an aneurismal bulge. Clinically, PCV
is associated with multiple, recurrent, serosanguineous
detachments of the RPE and neurosensory retina second-
ary to leakage and bleeding from the choroidal vascular
lesion
(17)
(Fig. 27). Although FA can sometimes confirm
the diagnosis of PCV, ICG angiography is the choice for
imaging this entity.
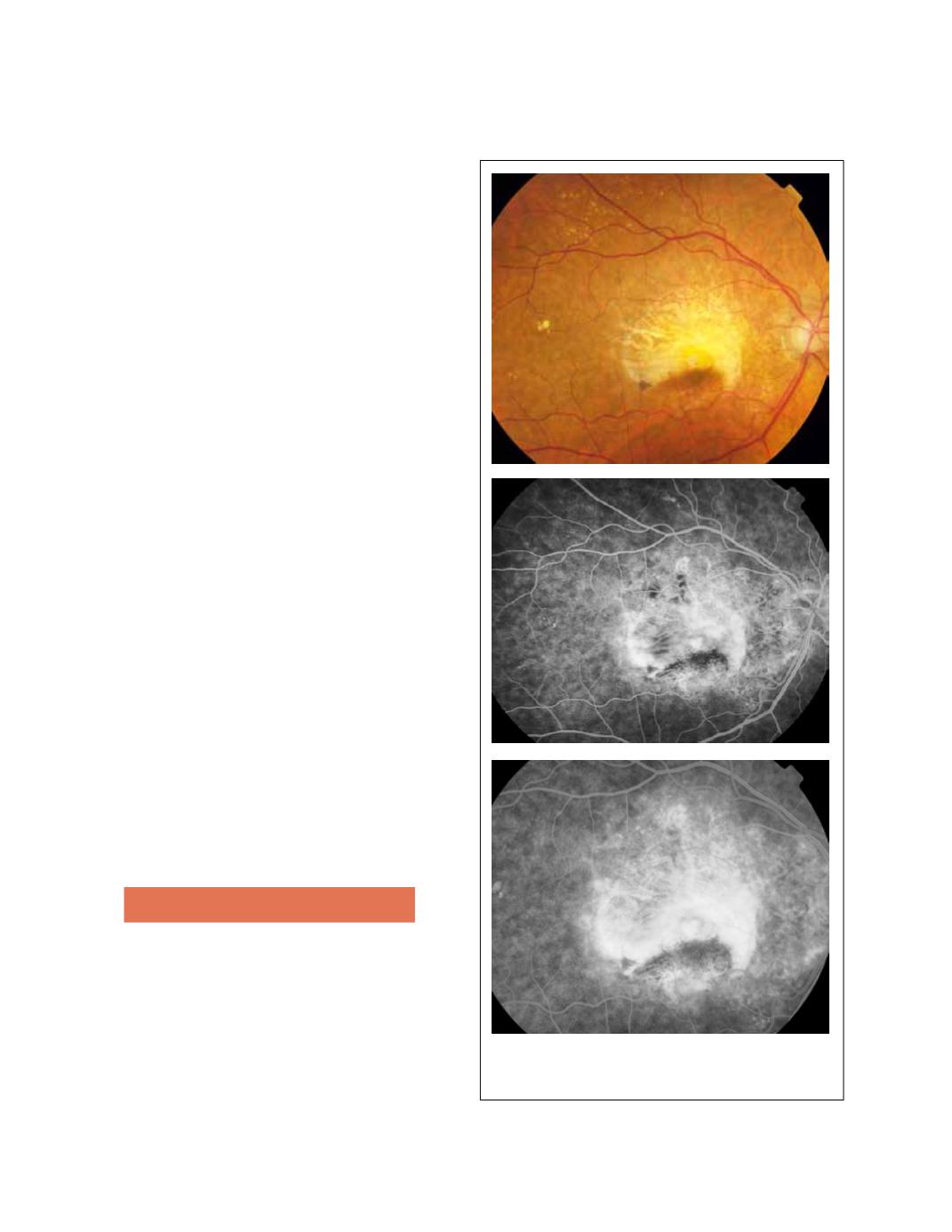
3.8 RPE tears
Although RPE tears can occur spontaneously, it is not
uncommon for them to occur after treatment with ther-
mal laser, PDT or antiangiogenic therapy. RPE tears are
commonly related to PEDs, although they have been
described in classic lesions too
(18)
. The detached mono-
layer of RPE scrolls toward the CNV, leaving a denuded
area of choroid exposed. On FA, the denuded area
becomes hyperfluorescent and the scrolled RPE is dark
and blocks the underlying fluorescence (Fig. 28).
3.9 Hemorrhagic AMD
FA is not very useful in hemorrhagic forms of macular
degeneration since blood blocks the underlying fluores-
cence (Fig. 29). ICG angiography can detect the pres-
ence of occult CNV.
3.10 Disciform scar
A disciform scar is the end-stage manifestation of
untreated CNV, namely formed by fibroblasts and
inflammatory cells. Angiographically, it typically shows
late staining (Fig. 30).
4. FA for monitoring AMD treatment
In the era of PDT with verteporfin, FA was the gold
standard for monitoring the response to treatment
(19)
.
Nowadays, with antiangiogenic therapy, OCT scanning
has replaced FA for this purpose since it is highly effec-
tive to detect lesion activity and it is a non-invasive pro-
cedure
(20)
. However, in some cases FA is still very useful
in the evaluation of treated patients.
Figure 28 - RPE tear.


