234
5. RPE Detachment
a. Hemorrhagic Detachment
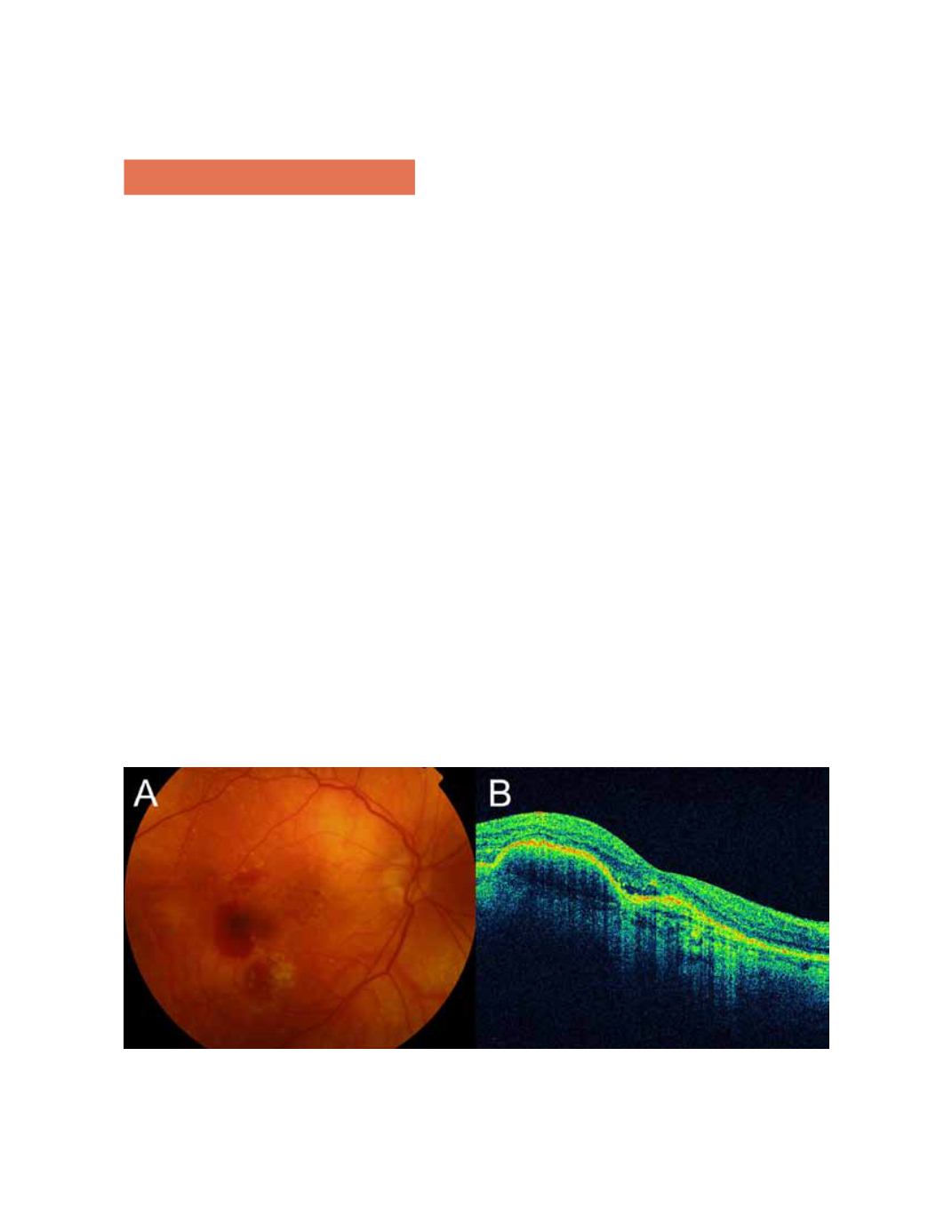
An RPE detachment can hemorrhagic in the presence of
neovascular membranes. Retinal hemorrhages often are
seen under the RPE. Detachment of the RPE forms a steep
angle to the choriocapillaris, and the accumulated blood
cells block penetration of the light rays from OCT in the
area of the detachment, so the penetration is minimal and
forms a shadow that hides the choriocapillaris and other
subsequent layers (Figure 5).
b. Serous Detachment
During development of exudative AMD, OCT shows
serous detachments of the RPE as optically clear areas
between the RPE and the choriocapillaris (Figure 6). The
detached pigment epithelium forms a steep angle with the
underlying choriocapillaris, which may be initially clear and
then contains cells and becomes blurred. A detachment also
can be single, multiple, dome-shaped, or bilobed.
6,8,24
c. Neurosensory Retinal Detachment
Active choroidal neovascular membranes cause edema and
small serous detachments of the neurosensory retina. The
membranes also can occur frequently in cases of pigment
epithelial tears (Figure 7).
Figure 5.
Hemorrhagic detachment of the RPE.


