104
Despite the works of Holz and Valkenberg, the prog-
nostic value of FAF remains controverse. In a recent
study, FAF was not a strong risk factor for develop-
ment or extension of GA
(50)
.
6. Clinical evolution
Eyes with GA may also develop CNV. In one study, 7%
of eyes with GA developed CNV in 2 years. The stron-
gest risk factor for developing CNV in one eye with GA
is the presence of CNV in the fellow eye
(51)
.
The 4-year rate of developing CNV is 11% if the other
eye has pure GA but increases to 34% if there is CNV. As
other forms of late AMD, GA tends to be bilateral (over
50% of cases) and there is high symmetry between eyes
for total atrophic area, presence of peripapillary atrophy
and enlargement rate
(51,53,58)
. On the other hand there is a
high interindividual variability
(54)
.
The mean overall enlargement rate of atrophic area is
2,6 mm
2
/year and eyes with larger areas of atrophy at
baseline tend to have larger enlargement rates
(53)
.
GA often first develops surrounding the fovea, sparing
the central area
(55,56,57)
. Because of that, the correlation
between visual acuity (VA) and area of atrophy can be
complex. The loss of three lines (ETDRS scale) was
observed by Suness et al. in 31% of studied eyes by 2
years and 53% by 4 years. The risk of acuity loss was
higher in eyes with better visual acuity at baseline and
with lightest iris color
(57)
.
Usually vision loss is bilateral because of lesion symme-
try, and evolution since first signs to legal blindness is
quite variable
(53,58)
.
Because of rods paucity, reduction of foveal cone func-
tion and also because of switching from central to eccen-
tric fixation, other visual functions as the contrast sensi-
tivity, reading rate and dark adaptation are decreased in
GA
(52,55,57)
.
The low luminance visual dysfunction and the maximum
reading rate seem to be significant risk factors for subse-
quent VA loss
(55)
.
7. Management
7.1 Prevention
In AREDS, dietary supplements as zinc and anti-oxidants
vitamins C, E and beta-carotene, have been shown
to reduce the risk of progression in participants in
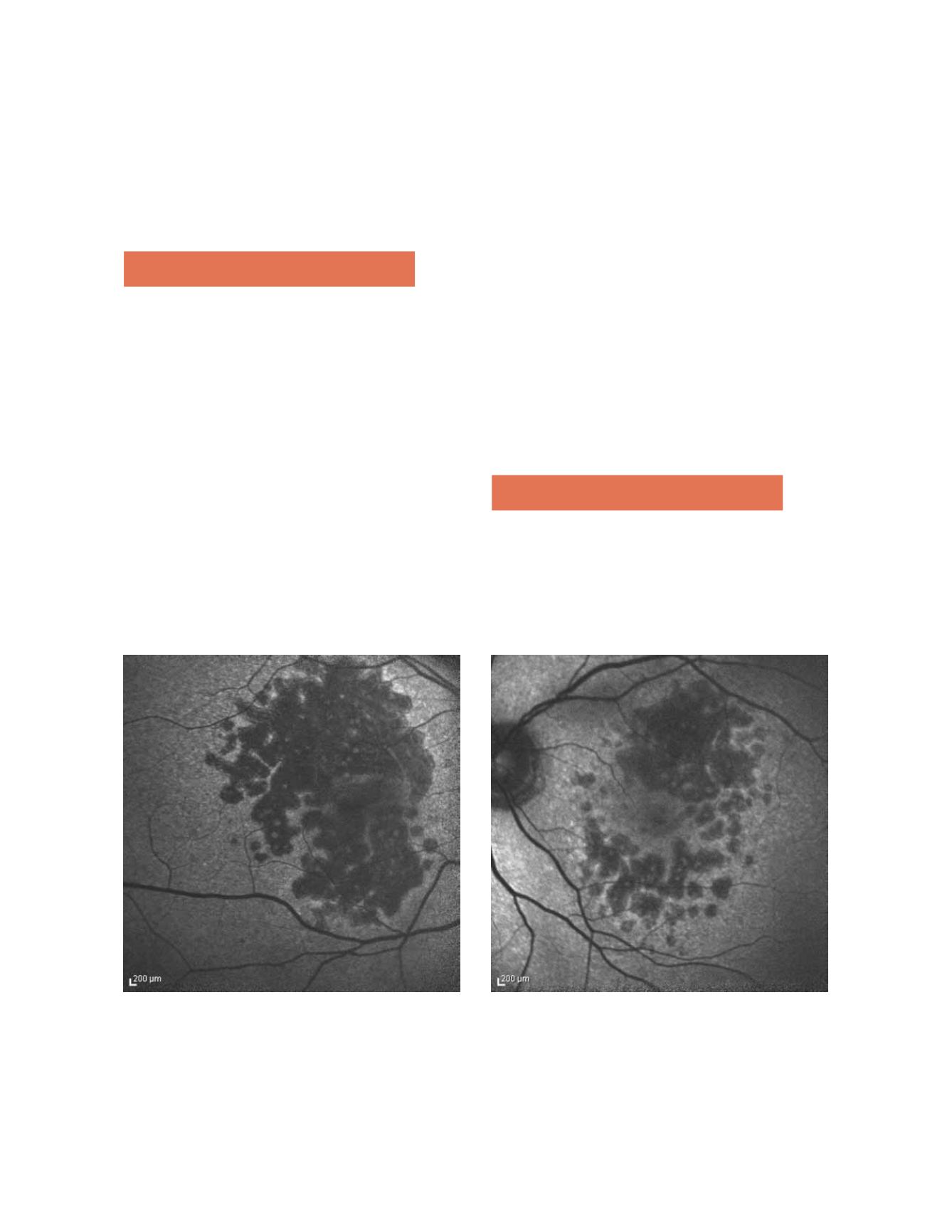
Figure 5. FAF showing increased fluorescence in the junctional zone around areas of atrophy.


